Combined with the precipitation forecast based on the NCFP GFS model on July 26, 2025 and multi-source data such as lithology, DEM and hydrological conditions along the Karakoram Highway, the TRIGRS model was adopted to conduct the landslide risk assessment in the northern area which is greatly affected by rainfall. The NCEP GFS precipitation forecast shows that the national rainfall will d...
Details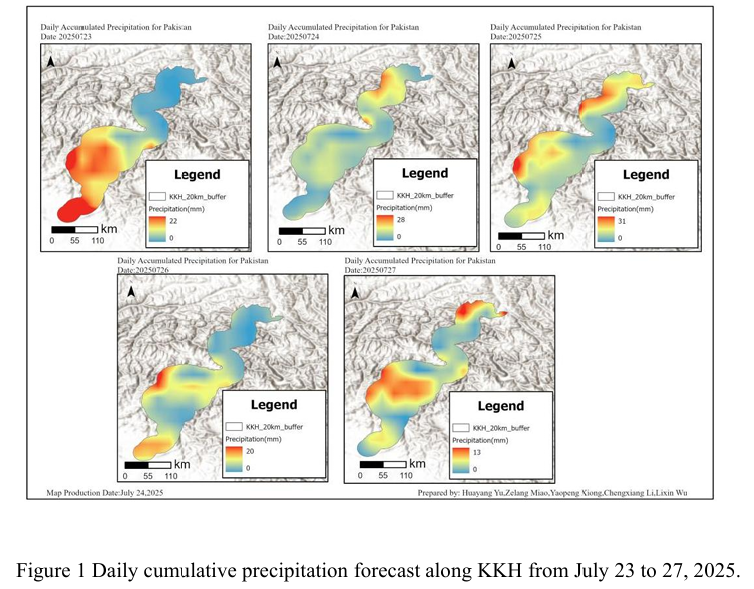
Combined with the precipitation forecast based on the NCFP GFS model on July 25, 2025 and multi-source data such as lithology, DEM and hydrological conditions along the Karakoram Highway, the TRIGRS model was adopted to conduct the landslide risk assessment in the northern area which is greatly affected by rainfall. The precipitation forecast of NCEP GFS shows that from Gilgit to Khyber in...
Details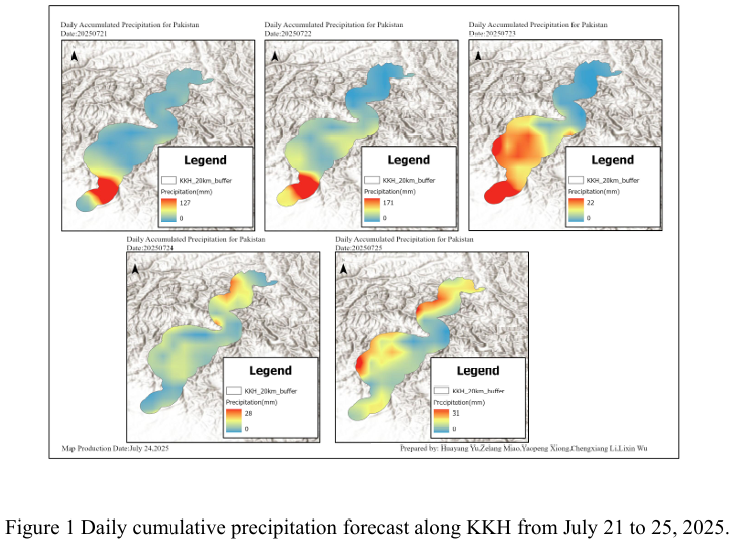
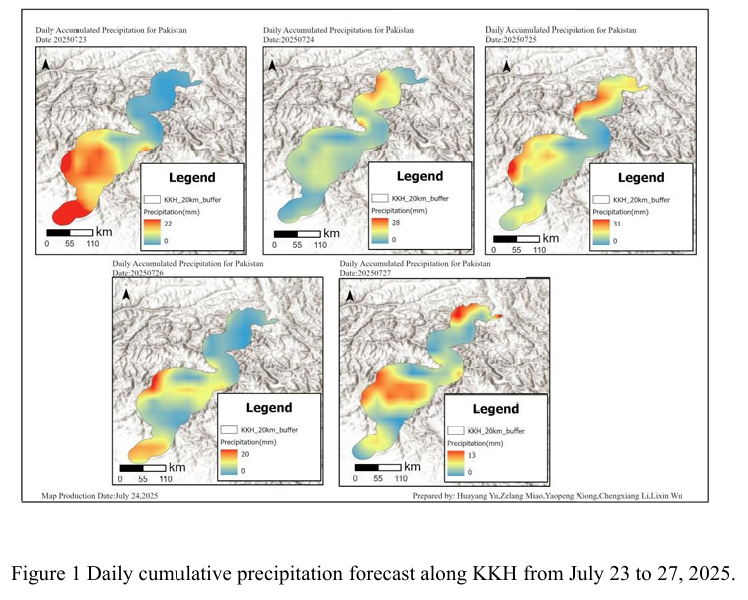
Combined with the precipitation forecast based on the NCFP GFS model on July 24, 2025 and multi-source data such as lithology, DEM and hydrological conditions along the Karakoram Highway, the TRIGRS model was adopted to conduct the landslide risk assessment in the northern area which is greatly affected by rainfall. The NCEP GFS precipitation forecast indicates that on July 24th, there will be ...
Details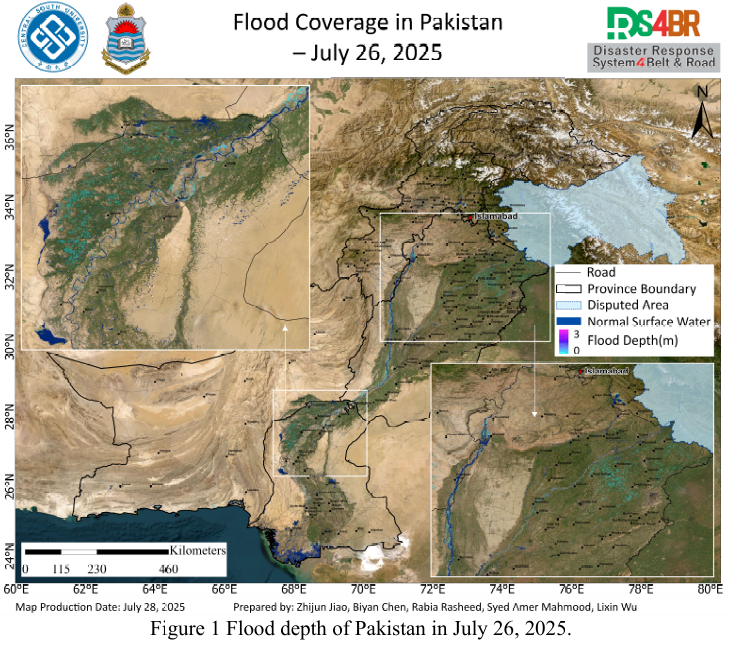
Based on multi-source remote sensing data acquired from July 16 to 27, 2025, including Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9, the flood extent and water depth across Pakistan were dynamically monitored and comprehensively assessed using the KDFIMv2 algorithm.Fig. 1 illustrates the spatial distribution of floodwater depth on July 26, 2025. The results indicate a general recession tren...
Details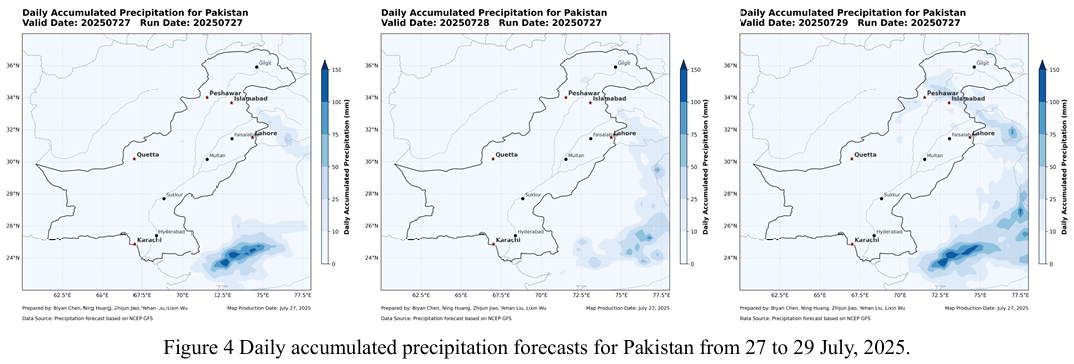
Based on multi-source remote sensing data acquired on July 25–26, 2025 from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9, the KDFIMv2 algorithm was employed to perform the latest dynamic monitoring and integrated assessment of flood inundation extent and water depth across Pakistan.Fig.1 presents flood water depth estimates for July 25, 2025. The monitoring results indicate a gradual reduc...
Details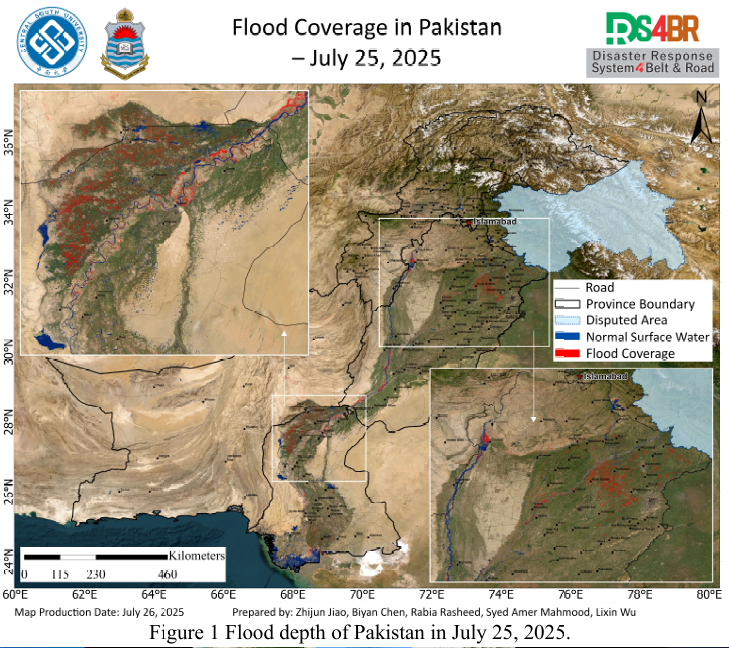
Figure 2 Cloud distribution observed by FY-4B at 3:00 and 10:00 UTC on July 26, 2025.Based on multi-source remote sensing data acquired on July 25, 2025—including Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9—the latest flood inundation extent across Pakistan was dynamically monitored and comprehensively assessed using the KDFIMv2 algorithm (Fig. 1). In parallel, FY-4B geostationary met...
Details
Based on multi-source remote sensing data from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat 8, and Landsat-9 acquired between July 23 and 24, 2025, flood depth (Fig.1) and inundation extent (Fig.2) across Pakistan were dynamically monitored and comprehensively assessed using the KDFIMv2 algorithm. Additionally, meteorological conditions and potential secondary disaster risks were analyzed using FY-4B geosta...
Details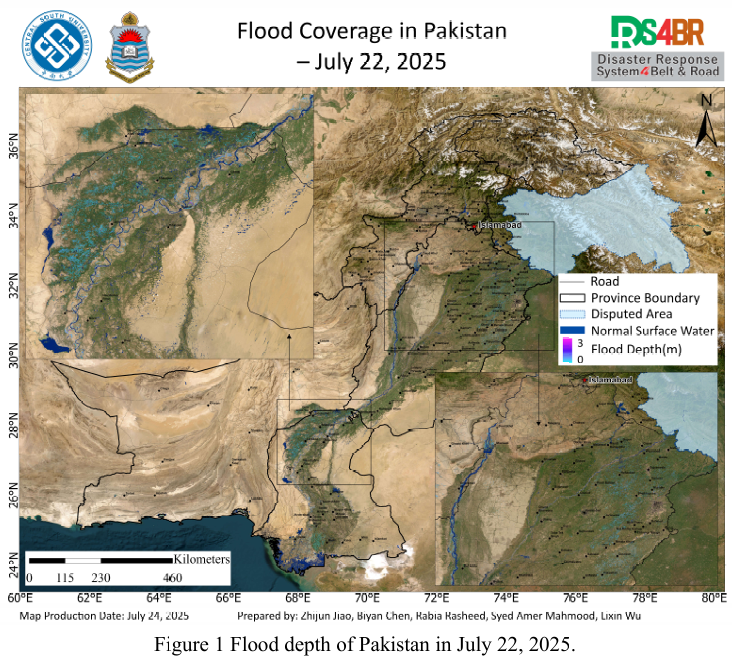
Based on multi-source optical and radar remote sensing imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9 acquired between July 22 and 23, 2025, and processed using the KDFIMv2 algorithm, a dynamic assessment and integrated analysis of flood depth (Fig. 1) and inundation extent (Fig. 2) across Pakistan has been conducted. Meteorological changes and future disaster risks were further ...
Details
Based on the optical and radar remote sensing imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel 2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9 acquired between July 21 and 22, 2025, floodwater depth (Fig. 1) and inundation extent (Fig. 2) across Pakistan were dynamically evaluated and comprehensively analyzed using the KDFIMv2 algorithm. Relevant meteorological changes and future risk trends were assessed based on FY-4B geostati...
Details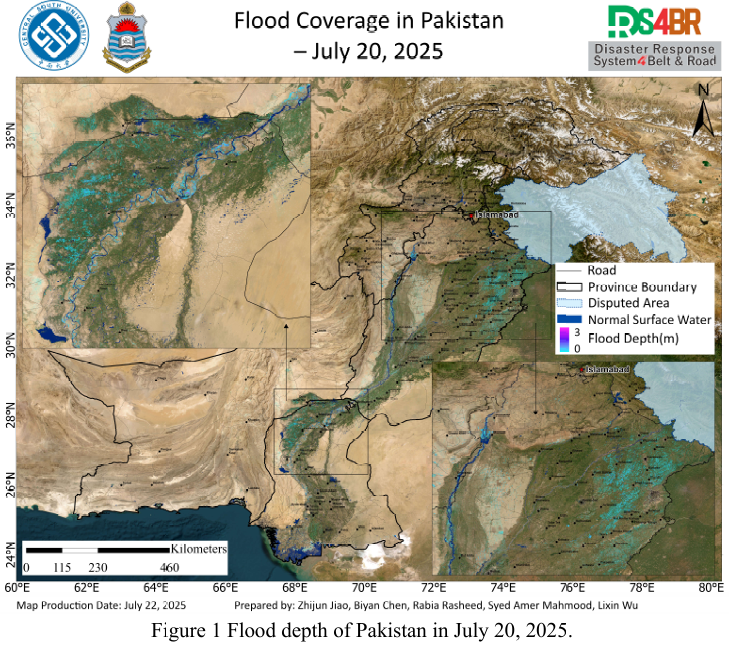
Based on remote sensing monitoring results from July 20 to 21, 2025, a comprehensive analysis and dynamic assessment of flood water depth (Fig. 1) and inundation extent (Fig. 2) across Pakistan was conducted. This analysis utilized multi source optical and radar satellite imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9, in combination with the KDFIMv2 algorithm.The flood water dep...
Details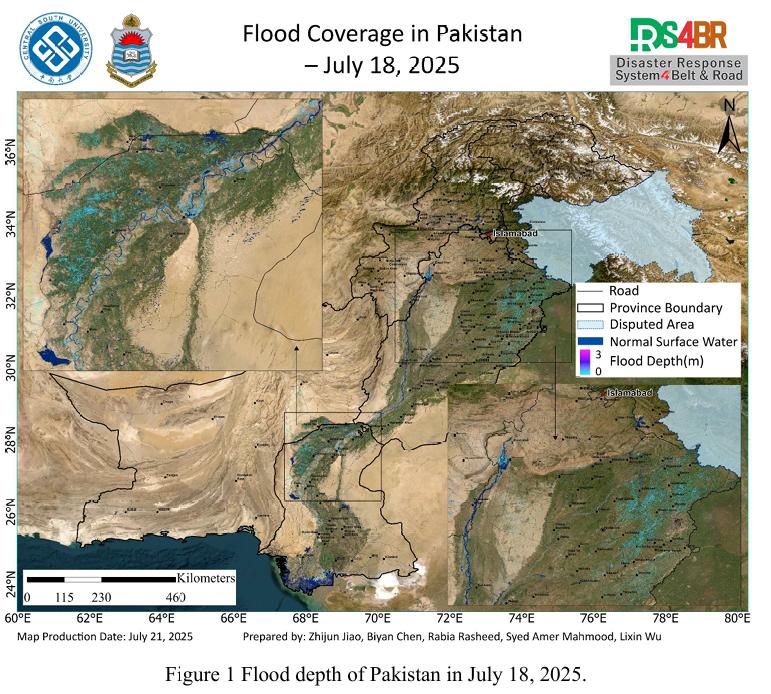
Based on remote sensing observations from July 18 to 20, 2025, a comprehensive flood assessment was conducted over Pakistan by integrating multi-source satellite imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9, and applying the KDFIMv2 algorithm for enhanced spatial flood analysis. The assessment focused on flood water depth (Fig. 1) and inundation extent (Fig. 2).The flood water ...
Details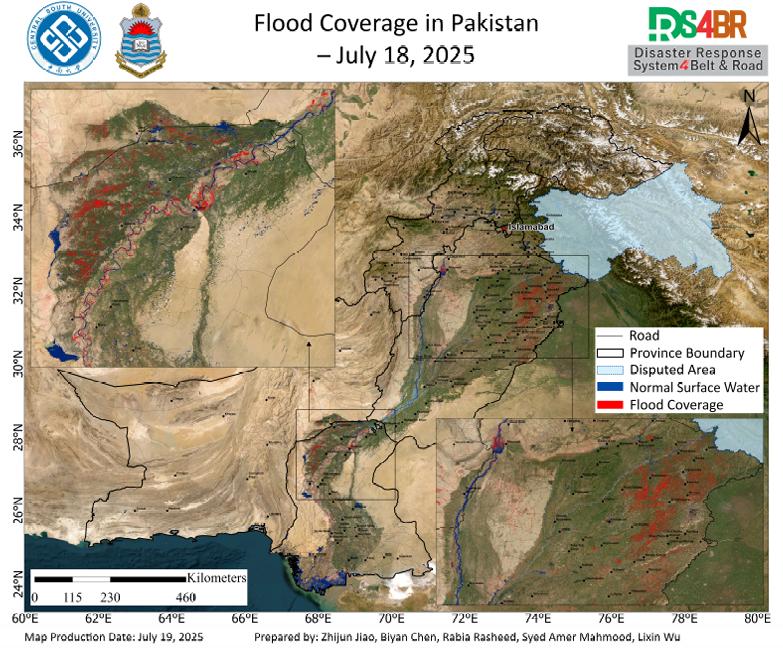
According to the remote sensing monitoring results from July 18, 2025, a comprehensive assessment of flood inundation across Pakistan was conducted using multi-source satellite imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9 (Fig. 1). The results indicate that flood-affected areas have continued to expand, with significant inundation observed across the Indus River Basin and surro...
Details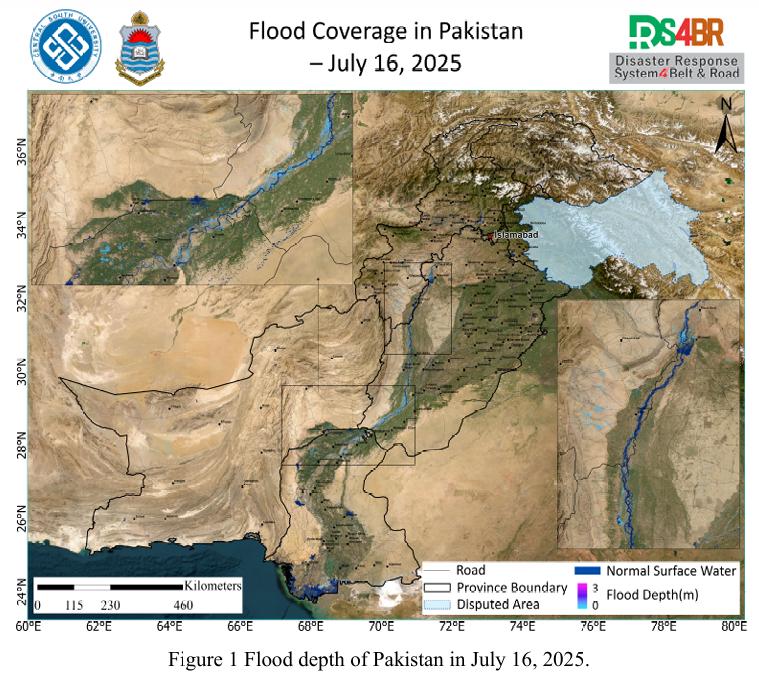
On July 16, 2025, a comprehensive flood depth assessment across Pakistan was conducted using multi-source satellite imagery from Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, and Landsat-9, integrated with the KDFIMv2 algorithm (Fig. 1). The results indicate that most inundated areas exhibited flood depths around 1 meter, while floodwaters in the main Indus River channel and the southwestern mountainous r...
Details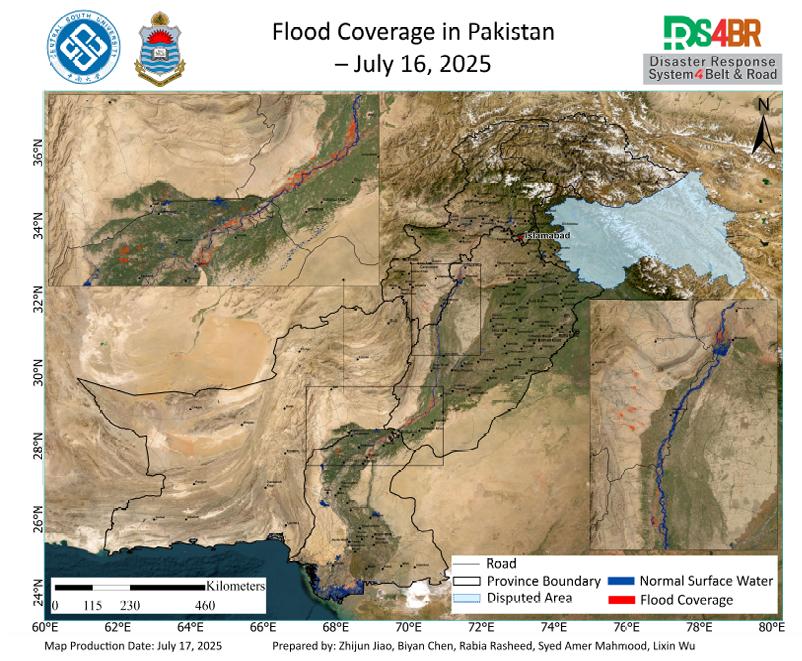
在2025年7月16日的巴基斯坦洪水遥感监测中,基于Sentinel-2、Landsat 8、Landsat-9 与 Sentinel-1 多源遥感影像,结合 KDFIMv2完成了对巴基斯坦全境 洪水淹没情况的综合评估(图1)。监测结果表明,洪水主要集中分布于信德省北 部及旁遮普省南部的印度河流域;这一地区地势相对低平,河网密集,历史上即 为洪水高风险区域。季风期间,来自上游的集中降雨和山区径流通过印度河主干 道向下游汇集,极易导致低洼平原发生广泛淹没。...
Details
Using multi-source remote sensing data acquired from July 15, 2025—including Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, Landsat-9, and Sentinel-1—and applying the KDFIMv2 algorithm, floodwater depth retrieval has been completed for the affected regions. Results from Fig. 1 indicate that floodwaters around the Chashma Reservoir have largely receded, with only minor residual inundation remaining. The flooded area ...
Details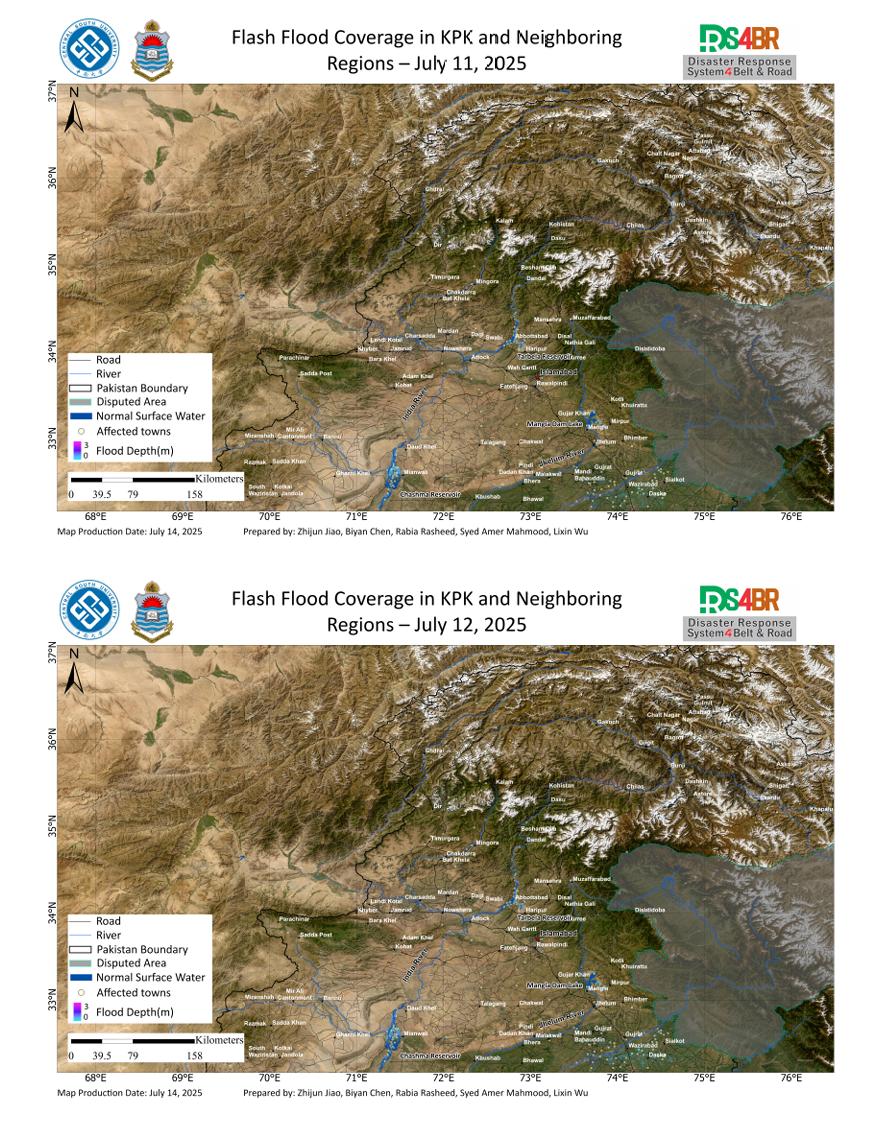
Using multi-source remote sensing data acquired from July 11 to 13, 2025—including Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, Landsat-9, and Sentinel-1—and applying the KDFIMv2 algorithm, floodwater depth retrieval has been completed for the affected regions. Results indicate minimal variation in floodwater depth around the Chashma and Tarbela Reservoirs, with no significant expansion of the inundated area. Howe...
Details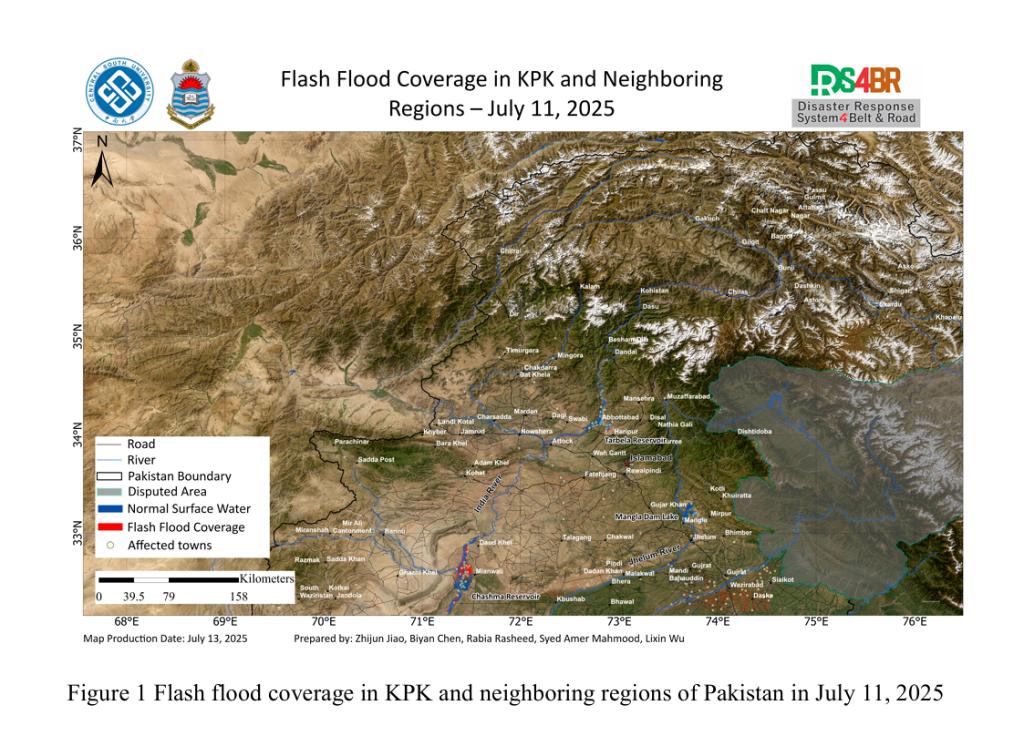
In response to the intense rainfall event affecting Punjab, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), and Balochistan, satellite-based rapid flood mapping was conducted to assess the impacted areas on July 11, 2025.Based on the KDFIMv2 algorithm, the distribution of natural surface water prior to the flooding was derived using multi-source satellite imagery from January to June 2025, including Sentinel-2, Lands...
Details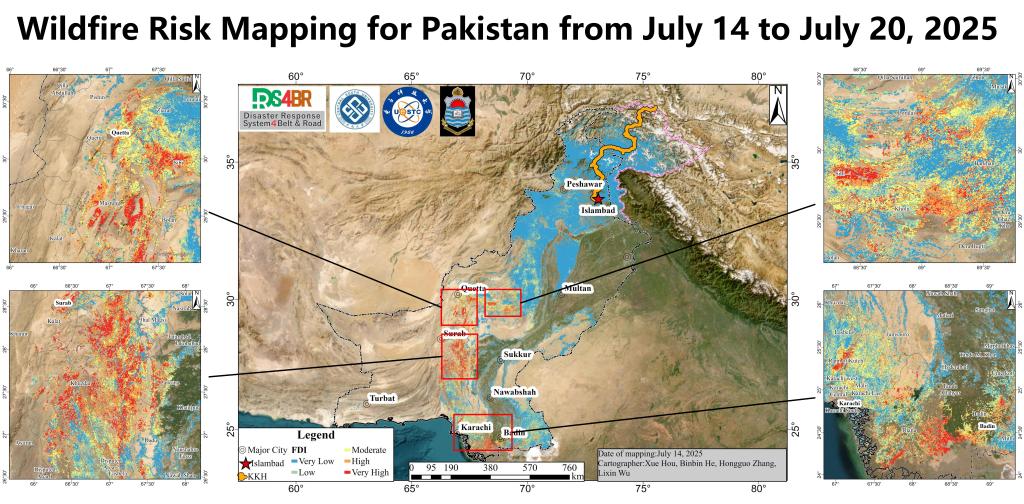
数据源:VIIR VNP43MA4\VNP43IA4数据;GFS数据火险分布情况:n Balochistan省(奎达、苏拉布、米斯图恩、博兰等)风险级别:高 - 极高,特别是在Quetta以南与Surab区域集中分布火险。n 信德省(Karachi、Badin、Thatta等)风险级别:中等 - 高,Karachi以北和东部的山区及Thatta附近有明显高火险分布。Karachi市区本身风险较低,但周边林地风险较大。n 北部地区(伊斯兰堡、白沙瓦、斯卡杜等)风险普遍较低,但某些局部高山地...
DetailsCopyright © 2025. DRS4BR All rights reserved.